Causes and signs of lumbar osteochondrosis - how does this disease manifest?
- Passive lifestyle. This includes people who lead a predominantly sedentary lifestyle. In a sitting position, the muscles of the corset relax, which increases the load on the lumbar spine.
- An inflammatory phenomenon located in the joints of the spine.
- The endocrine system functions incorrectly and hormones are imbalanced.
- Serious infectious diseases affecting bones and joints (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis).
- Gastrointestinal and cardiac dysfunction.
- Lifestyle associated with heavy manual labor (loaders, weightlifters, construction workers).
- Improper posture and improper walking.
- Poor cartilage tissue density (genetic factors).
- Congenital disorders related to the spine/skeletal structure. Deviations in the function of the musculoskeletal system.
- obesity.
- The work and rest system is unbalanced.
- age. After the age of 50 in humans, the intervertebral discs become inelastic and inactive.
- Chemical poisoning.
- flatfoot. With the correct foot structure, the load during walking is absorbed. If flat feet occur, the intervertebral discs are subject to the greatest load, leading to disc deformation and destruction.
- Back injury.
- Low back pain. Occurs due to sudden movement (jumping, running, coughing). The pain is paroxysmal in nature (low back pain). During this attack, the patient tilts the trunk forward and maintains this position for some time: trying to straighten causes a new wave of pain. Low back pain occurs due to pressure on the nerve roots.
- Lombardinia. The pain occurring in the lumbar region is increasing in nature. Initially, patients experience some discomfort, which may progress to severe, recurring pain. Lower back pain can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle and excessive physical activity. Low back pain can occur in the context of low back pain.
- Sciatica. Pain travels along the sciatic nerve. The main site is the lower limbs. This phenomenon occurs when the nerve roots of the spinal cord become pinched. If motor fibers are involved in the damaging process, patients will experience muscle spasms and muscle weakness. Ignoring these symptoms may lead to future muscle wasting.
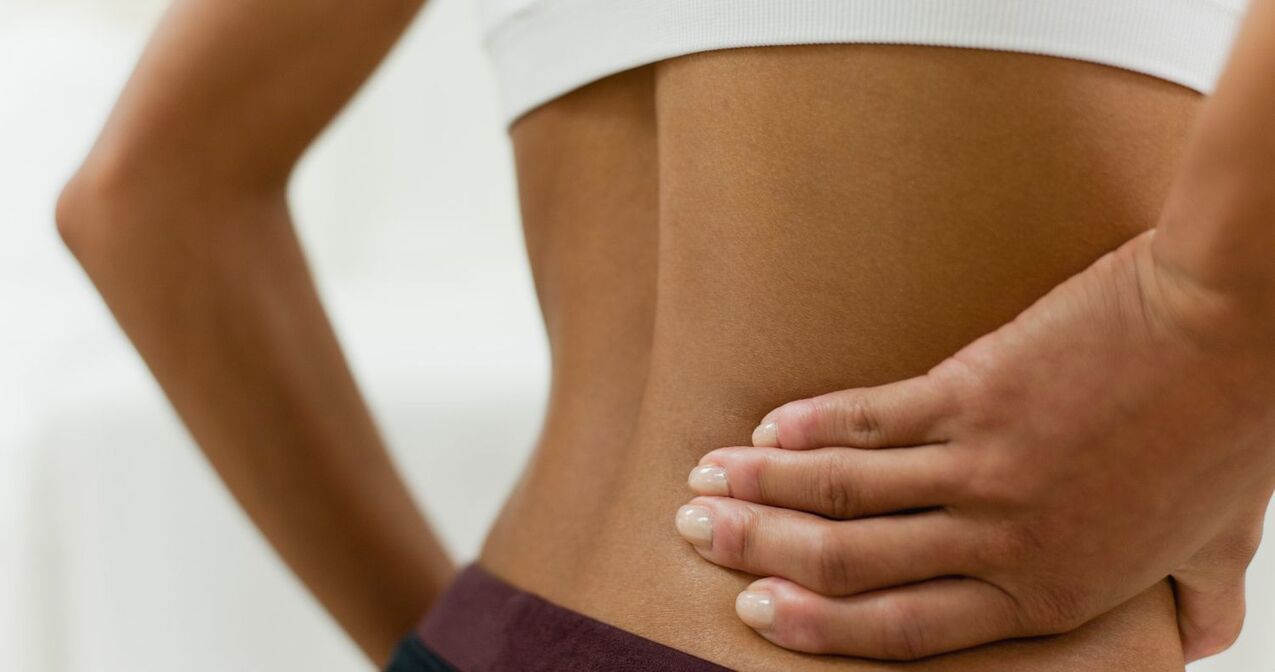

- Periodic loss of sensitivity of the skin on the legs;
- The patient complained of severe pain in the waist;
- Disturbances in the sweating system.
- Hot/cold lower limbs;
- Mild tingling/increased pain in the feet;
- Swelling (when the veins are compressed).
- Internal organ and genitourinary system dysfunction.
- Frequent fatigue.
- weakness.
- irritability.
Symptoms of lumbosacral osteochondrosis depend on the degree - how are the disease diagnosed?
1st degree lumbar osteochondrosis.
- Low back pain (lumbar pain) that occurs due to a tear in the disc (intervertebral) capsule.
- Tissue swelling.
- Muscle spasms.
- Frequent pain.
- Mimics diseases related to kidney and gastrointestinal function.
- Periodic abdominal pain that occurs against the background of abdominal muscle spasms.
Second degree lumbar osteochondrosis.
- Frequent pain (low back pain). The pain occurs in the lower back and may vary in intensity.
- Non-standard range of motion of spinal joints. A tight bandage around the waist can temporarily improve the patient's overall condition and reduce pain.
- Internal organ dysfunction (not always the case). In some cases, patients with lumbar osteochondrosis may develop bronchial asthma and biliary/urinary tract dysfunction.
- Pain in the lower limbs along the sciatic nerve.
Lumbar osteochondrosis third degree.
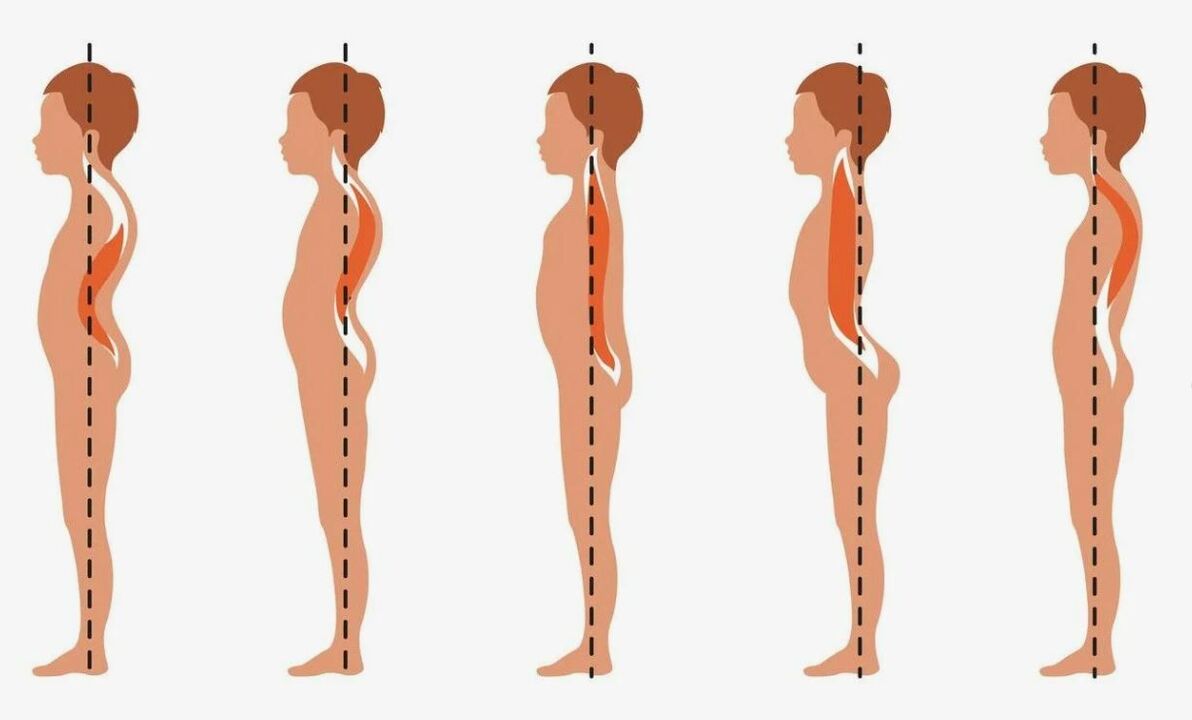
- Spinal deformities: curvature to the right/left (scoliosis); arching forward (lordosis), causing the lumbar spine to arch (kyphosis).
- Persistent, severe, acute pain that occurs with even the slightest physical activity (changing position, coughing, sneezing).
- Swelling of muscle tissue and ligaments.
- Periodic/periodic lack of sensation in the lower body (lower back, legs, feet).
- Urogenital system dysfunction.
Treatment methods for lumbar osteochondrosis
- To eliminate osteochondrosis of the waist, a comprehensive approach is required.
- Therapeutic measures (intensity, duration) will depend on the degree of neglect of the associated pathology.
Drug treatment of lumbosacral osteochondrosis—effective drugs
- Chondroprotectant. They prevent the destruction of spinal cartilage tissue that occurs in the early stages of the disease.
- Anti-inflammatory (nonsteroidal) medications. For the treatment of second-degree lumbosacral osteochondrosis. Medications from this group are available in the form of injections (intramuscular injection), tablets, ointments, rectal suppositories, capsules and solutions. If the condition worsens, the patient may be given an injection (16 mg/day)
- Muscle relaxants. Helps eliminate discomfort caused by increased muscle tone.
- Vasodilators. Helps improve blood circulation, prevent stagnation and minimize the risk of infection in the body.
- Local anesthetic. If severe, persistent pain occurs, the anesthesiologist will perform a blockade. A special needle is used to inject the solution into the painful area. The pain goes away immediately and won't bother you for weeks. This kind of blockade should only be used in extreme cases: it can have many negative consequences.
- Vitamin and mineral complex. Often used in elderly patients to increase the strength of tendons and ligaments.
Massage for lumbosacral osteochondrosis
- caress. There are several types of strokes: hook, horizontal, fan-shaped, ending in a symmetrical stroke in the area of the sternum muscles.
- extrusion. Combined with stroking. This massage technique ensures muscle stretching.
- Knead.
- shake.
- Grind. Often used to improve the function of tendons, ligaments, and joints.
- Point impact. Not every massage therapist is able to perform this procedure using acupressure techniques.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine Gymnastics or exercise therapy - a set of exercises for the lumbosacral spine in the video.
Physical therapy for lumbar osteochondrosis
- cancer;
- Acute phase of osteochondrosis;
- Severe impairment of central nervous system function;
- Injury to an area that should receive physical therapy.
- UV radiation. Heating the pathological area helps improve blood supply, eliminate spasms, and eliminate pain.
- Magnetic therapy, electrophoresis. Application of this method involves exposing painful areas of the spine to magnetic/electric fields. Through this action, the body's metabolic processes are established, inflammatory phenomena are eliminated (completely/partially), and recovery is accelerated.
- Laser Treatment. Due to the influence of the helium-neon emitters, the condition of the affected spinal roots improved significantly.
- Balneotherapy. The main ingredients used to perform related physical procedures are therapeutic mud and mineral water.
- Decompression therapy (mechanical stretching of the spine). Associated with severe back pain.
Folk remedies for lumbar osteochondrosis
- Red pepper tincture: used to rub painful areas in the lower back. To prepare the medicine, you need to mix 1 tbsp. Vodka (diluted with medical alcohol), 20-25 g dry red pepper powder. These ingredients need to be soaked (stirring occasionally) for 5-7 days.
- Camphor and mustard: Apply daily before going to bed. To prepare this product, mix mustard powder (50 g), camphor alcohol (50 ml), medical alcohol (90-100 ml), beaten egg whites (3 pieces). After mixing well, you should have a liquid ointment.
- Honey and Aloe Vera: Use for lower back compression (2 times daily). To prepare this product you need honey (100 ml), dilute medical alcohol (150 ml), aloe vera juice (50 ml). The mixture should sit for 10-12 hours before use.
- Horseradish and Alcohol: Use on affected areas of the back. To prepare this product, mix horseradish root juice and medical alcohol in equal proportions. After wiping, wrap the treated area.
- Garlic juice and lard (1: 2): used to rub painful areas on the lower back.
- Cabbage leaves peeled from their thick veins: used for compresses. Cabbage leaves should be soaked in hot water (not exceeding 60°C) before use. You can use a bandage/gauze to secure the leaves to your lower back. Once the leaf color has changed, the process can be repeated.

Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Fish (sea).
- Vegetable fats (olive oil, flaxseed oil).
- Dairy products with the lowest dye and sugar content.
- Dishes containing gelatin (aspic, jellies).
- Animal cartilage (can be used to prepare first dishes).
- Fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Greenery.
- mineral water.
- swim.
- Take a daily walk.
- Gymnastics exercises (also suitable for pregnant women).