Classification and reasons
- Autoimmune diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, scleroderma, etc. ;
- Inflammation of joints caused by certain infections (syphilis, gonorrhea, encephalitis);
- Genetic disorders of the musculoskeletal system and joints, mutations in type 2 collagen.
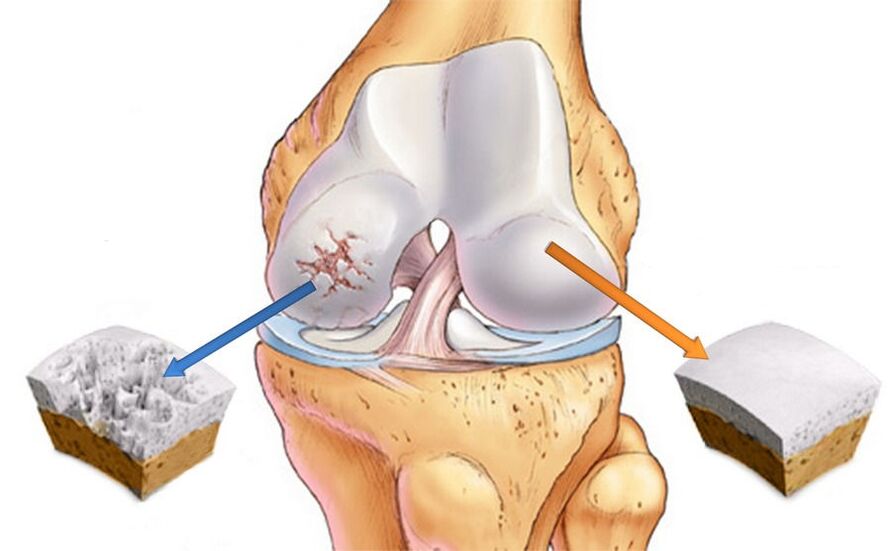
- Old age, overweight, osteoporosis;
- Hormonal changes, including reduced estrogen synthesis in postmenopausal women;
- Metabolic diseases;
- Lack of trace elements and vitamins in the diet;
- congenital and acquired skeletal malformations;
- hypothermia and poisoning with toxic compounds;
- Persistent joint injuries during sports training or hard work;
- Knee surgery - for example, removal of the meniscus.
symptoms and stages
diagnosis
treat
NSAIDs and corticosteroids
Chondroprotectant and hyaluronic acid
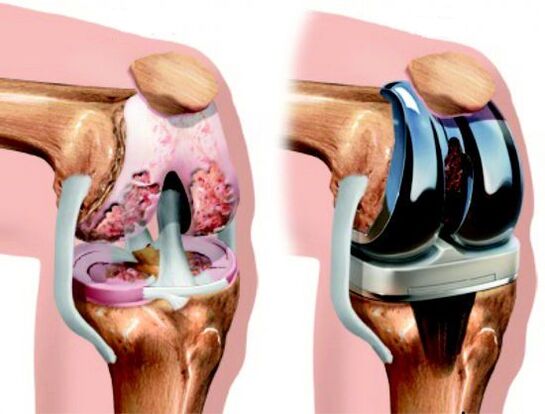
Surgery
important:Arthroscopy can be used not only for treatment but also for diagnosis of joint pathology. This process allows you to identify damage that would otherwise be undetectable.

physiotherapy
- magnet therapy;
- Mid-wave ultraviolet (WUV);
- Infrared laser;
- UHF;
- ultrasound;
- diameter and sinusoidally modulated current (amplified pulse therapy);
- Darsenval.