cause of pain
- Genetic susceptibility.Having a close relative with osteochondrosis, especially at a young age, increases the risk of its early onset and complications.
- Lack of physical activity.A sedentary lifestyle can destroy the nutrition of the intervertebral discs. They have no blood vessels and obtain nutrients by diffusion from the vertebral bodies. These processes occur actively during physical activity.
- Injuried.Spinal injury accelerates the development of degenerative changes in the spine.
- Uneven loading of the spine.Possible situations: Improper movements, poor posture, primary load on one side of the body or one limb, long tilted head postures (e. g. when looking at a mobile phone).
- Metabolic disorders.The condition of the vertebrae is affected by endocrine diseases, especially diabetes, which makes tissue nutrition difficult.
symptom
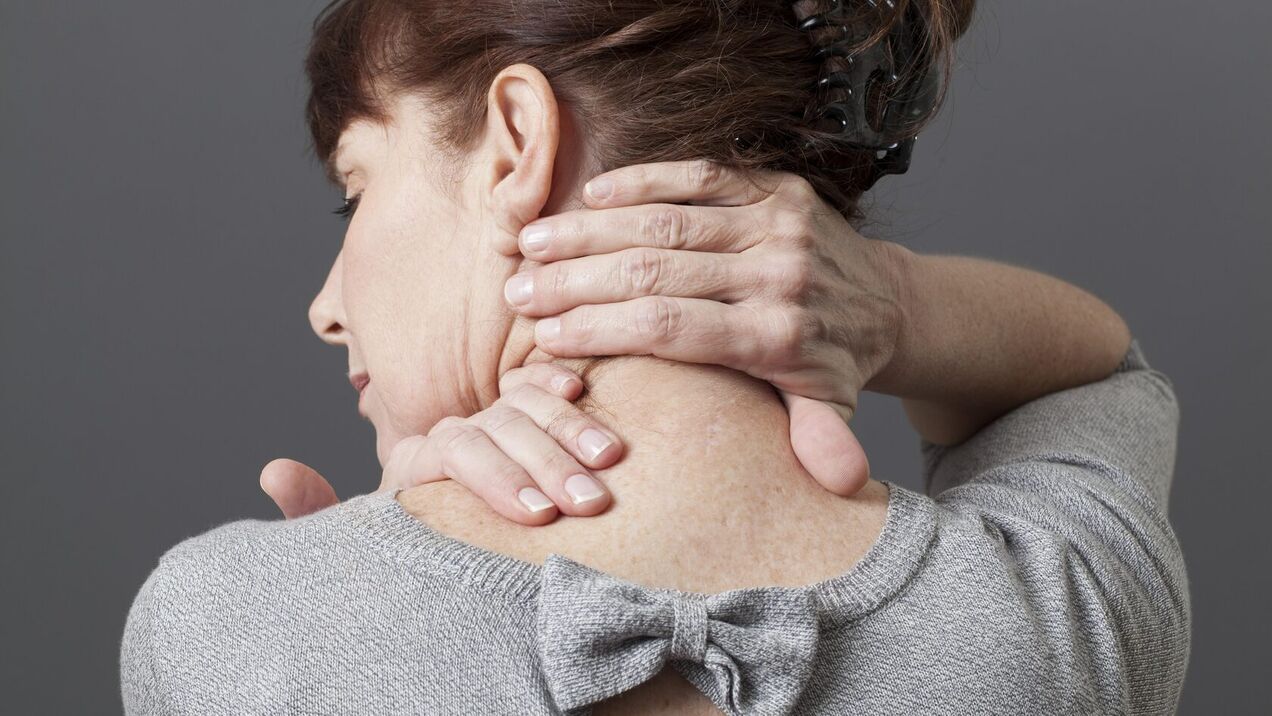
The main symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is pain. Its localization depends on the nature of the lesion. Pain in the neck can be felt and is associated with reflex muscle spasms when irritated by osteophytes from herniated discs or sensitive ligaments. If the hernia compresses a spinal nerve, pain may radiate into the arm.
- Neck movement is limited and pain occurs when turning the head.
- Neck muscle spasm.
- Decreased upper limb muscle tone and strength are typical symptoms of vertebral root compression.
- Impaired skin sensitivity of upper limbs.
- When a vertebral artery hernia becomes compressed, symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency may occur, which develop acutely when turning or tilting the head: dizziness, nausea, tinnitus, fainting, short-term memory impairment, unsteady walking, visual impairment, hearing and speech impairmentDisorders, severe muscle weakness in the limbs.
diagnosis
- Laboratory tests (general blood counts, biochemistry blood tests, urine tests, others - as indicated).
- X-rays of the cervical spine to check for fractures and other injuries.
- A CT scan of the cervical spine can identify injuries, cancer, and other changes in the vertebrae.
- Cervical spine MRI evaluates the condition of the spinal cord, nerve roots, and visualizes herniations and hernias.
- Neuroelectromyography determines the conduction of impulses along the spinal cord roots.
When can it be treated without surgery?
conservative treatment
- acupuncture.The neurologist uses a special sterile needle to stimulate the biologically active points. This can provide relief: reduce pain and relax muscles.
- Plasma therapy.By giving patients platelet-rich plasma topically, the regeneration of damaged tissue can be stimulated. Reduced recovery time after surgery, illness and injury.
- High strength magnet.Electromagnetic fields stimulate and accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue. Relieve pain and reduce swelling.
- Physical therapy laser.This method has anti-inflammatory, anti-edema, and analgesic effects. It reduces the size of the hernia. It is used as a basic method as part of the process of absorptive treatment of intervertebral hernias.
- physiotherapy.Classes are designed to strengthen muscles, increase spinal flexibility, restore range of motion to spinal joints, and develop correct posture. After acute pain relief, experts will individually select exercises for the patient.
- Intramuscular Theo Taping.Combined with physical therapy. Before class, the doctor places tape on the neck and collar area in certain directions to relax the muscles and affect the pain receptors. As a result, the pain is reduced. With regular use, spinal mobility is restored and muscle tone returns to normal.
- Medical massage.Experts relieve muscle spasms by acting on receptors in the skin, muscles and fascia. Get fast, permanent pain relief and improved spinal mobility.
forecast
prevention
- Maintain optimal weight.
- Maintain an active lifestyle.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress and pillow.
- Engage in regular moderate physical activity - half an hour of walking every day and a warm compress on your neck and back are enough.
- Workplace ergonomics. The desk and chair should be appropriate for your height, and the computer monitor should be at eye level or slightly higher.
Summary:
- Cervical osteochondrosis is a degenerative dystrophic change of the vertebrae, accompanied by the formation of intervertebral disc herniation.
- Cervical osteochondrosis presents with neck pain, limited mobility, and muscle spasms. When the root of the spine is compressed by a hernia, muscle weakness and numbness of the skin of the upper limbs may occur.
- The diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis includes examination by a neurologist and additional tests as necessary: spine CT, MRI and other methods.
- Treatment for osteochondrosis is usually conservative and aims to relieve pain, inflammation, and muscle spasms.
- Prevention of osteochondrosis includes maintaining an active lifestyle, regular physical activity, and workplace ergonomics.