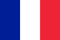
Arthropathy is a pathology in which joints are gradually deformed. In the initial stage, cartilage and ligaments are destroyed. The process is slow, so the disease is already detected at a later stage of development. In the future, this could lead to reduced mobility and disability.
The risk of developing osteoarthritis increases with age. The disease affects both men and women equally.
symptom
Joint pain during exercise is the main symptom of the disease, so many people seek immediate medical attention. Discomfort can occur when walking for long periods of time or exercising vigorously.
What is joint disease, doctors will tell you when diagnosing the disease. Pathology is suspected when the following symptoms are present:
- Nocturnal pain due to stagnant blood in the veins and increased intra-articular pressure;
- Tightening due to friction of collapsed cartilage;
- Increased pain with heavy load, especially knee arthropathy during squatting, exercise (running, jumping, weight lifting), weight bearing;
- Weather dependence, when the affected joints start to ache when the weather changes, especially before rain or heavy snow, cold snaps;
- Morning stiffness.
Difference Between Arthritis and Osteoarthritis, Doctor's Answer
A doctor and popular health TV host said the terms "arthropathy" and "osteoarthritis" refer to a condition in which cartilage is damaged and bone tissue grows.
With arthropathy, the cartilage tissue on the surface of the joint is destroyed, the movement of the limbs is limited, and severe pain occurs. Pathological diagnosis is made in men and women over the age of 40 (the main cause in women is the onset of menopause, when hormonal changes occur in the body).
Osteoarthritis manifests as articular cartilage deforms and affects bone tissue, affecting the entire joint, resulting in disability.
Other diseases with similar symptoms
There are many diseases with symptoms similar to arthropathy:
- Frozen shoulder, cervical osteochondrosis, osteoporosis and shoulder arthritis.
- Elbow epicondylitis, osteoarthritis deformity, rheumatoid arthritis of the hand.
- Hip disease.
- Rheumatoid and septic arthritis in children.
Types of Arthropathy (By Location)
The type of disease depends on the location of the affected joint. The mildest type of pathology is the shoulder. Osteoarthritis can be diagnosed with:
- neck area;
- Knee joints (affects both legs, but develops to varying degrees);
- ankle;
- Hip joint (pathological features of the elderly).
cause of disease
The disease can develop without a cause (idiopathic or primary). Pathological processes in the body often trigger a second form of pathology. Causes of joint disease:
- Injuries (dislocations, bruises, fractures, torn ligaments, meniscus injuries);
- Congenital abnormalities of joint development (dysplasia);
- metabolic diseases;
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- Inflammatory processes (acute septic arthritis);
- Infectious diseases (TB, encephalitis, gonorrhea, syphilis);
- Endocrine system pathology (thyroid disease);
- hemophilia;
- age-related changes in the body;
- Often hypothermia.
diagnosis
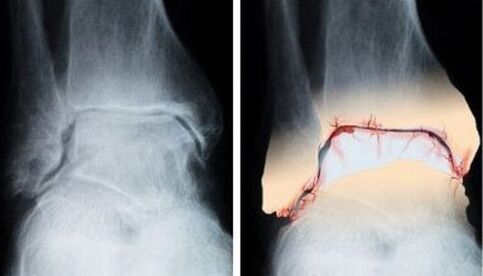
There are several diagnostic methods:
- X-ray examination;
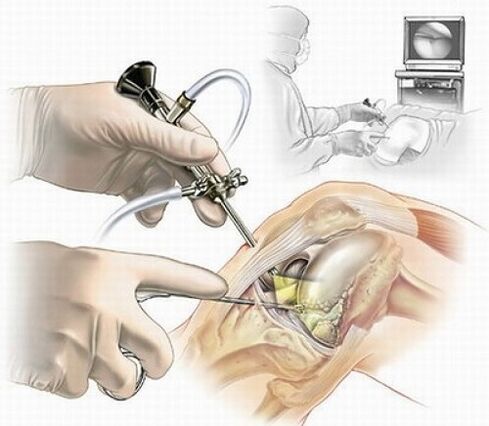
- Arthroscopy (inspection with a video camera inserted into the joint through a 4-5 mm incision);
- blood analysis;
- Histological examination of the synovium (arthropathy, non-regeneration of epithelium, appearance of atrophic villi, reduced number of blood vessels).
Degree of joint damage
Use classification, including grade 4 of disease progression.
Stage 1 (disease does not affect the ability to work):
- Joint movement is only slightly restricted in one direction;
- no bone growth on the x-ray;
- uneven surface of cartilage;
- The joint space begins to narrow.
The second stage (affecting work ability):
- average movement limit;
- Strong crunching when changing limb position;
- Partial atrophy of nearby muscles;
- bone growth, osteophytes;
- Clearance has 2-3 times less lumens than standard.
Stage Three (Disability):
- joint deformities;
- restricted movement;
- Pain during exercise and at rest (relief with painkillers);
- no joint space;
- muscle atrophy;
- Ossification of the articular surface.
Fourth stage:
- Severe pain that doesn't go away after taking painkillers.
- Complete destruction of the joint.
basic treatment
Arthropathy treatment includes several approaches. For a positive result, it is necessary to take medication, monitor weight. Physiotherapy, exercise therapy are prescribed. In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed.
medical
The main task of treating arthropathy is to eliminate pain. For this purpose, different groups of drugs are prescribed:
- NSAIDs in the form of tablets, suppositories, ointments, gels, injections. Long-term use of these drugs can adversely affect cartilage tissue.
- corticosteroids. They are used in severe cases to relieve pain and do not slow the progression of the disease. With uncontrolled use, cartilage thins.
- Analgesics, antispasmodics. Not great at relieving inflammation, but effective at relieving pain.
- chondroprotective agent. These are the main drugs in the treatment of joint diseases, they provide nutrients to the cartilage tissue and stimulate cell regeneration. They have no immediate effect, and the condition of the joints gradually improves. Works even in stage 3 of the disease.
- Vasodilators. Need to improve blood circulation and eliminate spasm of small blood vessels. Improves the action of chondroprotective agents.
physiotherapy
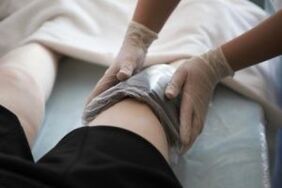
For joint diseases, physical therapy can be used effectively. The procedure includes heating the joints. Dry heat slows the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue, reduces pain and improves the general condition of the patient.
The following methods are used to treat the disease:
- Ultrasonic shock. High-frequency sounds act on body tissues, producing many beneficial effects. With micro-massage, the muscles are warmed, the blood flow in the capillaries is improved, and the metabolic process is accelerated.
- electrophoresis. Under the action of a low-voltage current, the drug is injected into the problem area without affecting the rest of the body.
- Magnetic therapy. Application of this method helps reduce inflammation, strengthen blood vessels, improve blood flow, and accelerate cellular regeneration in problem areas.
- Radiation exposure (using infrared, ultraviolet or laser radiation). It is used as an adjunct to other physical therapy methods or when there is a contraindication to its use.
surgical
In the absence of positive motivation for arthropathy treatment, the use of surgical methods:
- Operational intervention. There are 4 types: joint preservation, joint replacement, joint resection, joint strengthening. The choice depends on the degree of disease progression, the intensity of pain, and the individual characteristics of the patient.
- prick. It is performed in the presence of progressive arthropathy. It performs 2 functions: relieves pain in damaged joints and relieves tension within the capsule, which removes substances that damage cartilage tissue from the capsule. It is an informative diagnostic method. During this procedure, medication is injected into the joint after local anesthesia.
- Arthroscopy. Usually done on an outpatient basis. During surgery, portions of cartilage or bone can be removed from the joint, the meniscus can be treated, ligaments can be rebuilt, and joint surfaces that have been deformed during arthropathy can be cleaned. It is performed under general or local anesthesia.
- Arthrotomy. Joint opening is performed if arthroscopy does not give a positive result. It is used for long-term joint swelling and persistent severe pain that the medication cannot stop. This is recommended if you want to remove large pieces of cartilage or bone tissue.
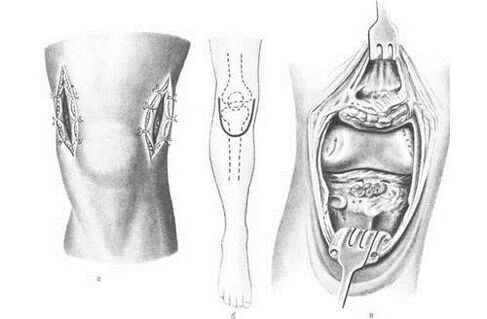
An operation to change the position of a joint where correction of the position of the bone is required, and the joint structure is defective in order to prevent arthropathy.
exercise therapy
When the joint is not yet deformed, physical therapy exercises can help with the initial stages of the disease. Active exercise slows the progression of the disease, but with joint damage, when the disease progresses to an advanced stage, physical activity can lead to deterioration and destruction of tissue in the problem area.
You will need to do this after consulting an expert who will help you choose a set of exercises and master the implementation. The first training should be conducted under the supervision of an instructor.
When doing the exercises, you must follow these rules:
- Avoid putting pressure on the injured joint.
- Moderate movement speeds do not cause joint damage.
- Rest and exercise must be balanced.
- High-load and high-intensity exercise can increase pain and cause joint swelling.
- In any position of the body, correct posture needs to be remembered.
Regular exercise with exercise therapy can help increase range of motion, relax muscles, and improve a patient's general condition.
manual therapy
Combined with medications for arthropathy, manual treatments are used to increase the mobility of damaged joints, prevent muscle wasting, and have a positive effect on the patient's entire body.
During a session, the following actions are performed:
- Muscles involved in the work of the diseased joint relax (completely relax).
- Perform low-frequency activities on the articular surface to expand the range of motion of the joint to the limit of activity.
- Do acupressure according to the Schwartz method to rest the muscles.
- Treatment with lasers and instruments.
Ethnoscience
Folk remedies are actively used in the treatment of arthropathy to activate the production of collagen - the basis of tendons and cartilage. They can also relieve joint swelling and reduce pain. Recipes include plants such as thyme, clover, dandelion (root), strawberry and birch leaves, and willow bark.

There is a simple but effective way to use birch leaves. To do this, you need to choose comfortable clothing that fits snugly in the area affected by the arthropathy (high socks or stockings for the ankles, tights for knee treatment, tight tights for the hip). At night, you need to cover the diseased joints with leaves and wear appropriate clothing. You can't wrap fabric in polyethylene.
The leaves suck salt, toxins and cholesterol deposits from diseased joints, leaving the skin smooth and soft after surgery. The course of treatment is 6-7 procedures, you need to consult a doctor before use, because. There may be contraindications to use.
In folk medicine, ointments, infusions, freshly squeezed juices, compresses are used to combat joint diseases, and doctors often recommend their use in combination with medicines. All non-traditional treatments work to reduce pain and swelling in damaged joints, repair tissue and improve the general condition of the patient.
But do not self-medicate, otherwise complications may occur.
Do you need to adjust your diet
In arthropathy, it is necessary to adjust nutrition, the purpose of which should be to improve metabolic processes, lose weight if necessary, strengthen connective and cartilaginous tissues and ligaments. No special diet. For a good therapeutic effect, the following rules must be followed:
- Consider the calorie content of meals to maintain stability in normal-weight patients and return to normal in overweight patients.
- Fats, smoked dishes, semi-finished products containing flavor enhancers, dyes and preservatives are prohibited.
- Products should be natural: low-fat fish and meat, seafood rich in minerals and vitamins, fresh fruits and vegetables, hard cheese, butter, low-fat cottage cheese, nuts, eggs, rye and bran bread, High quality vegetable oil rich in unsaturated fatty acids.
- It is necessary to limit the daily intake of salt to less than 8 grams.
- Drink at least 2-2. 5 liters of water every day.
- Include foods with natural chondroprotectants in your diet: lean chicken, cartilage, red fish, hard cheeses. The increased use of gelatin normalizes the structure of cartilage tissue, strengthening it. To do this, you need to add a variety of jellies, jellies, frozen fish, kisels to your menu.
- Unloading takes 2-3 days per week (cheese, kefir, fruit and vegetable days).
What are the hazards of different stages of the disease?
In the initial stages of the disease, arthropathy manifests as periodic pain and limited mobility in the joints. The danger of the disease is that, if you ignore its initial symptoms, then in the subsequent stages of development, the pathology will lead to the destruction of joint tissue. Consequence - complete loss of liquidity. Patients were assigned to disability groups based on disease progression and joint condition.
prevention
Prevention of joint disease is as follows:
- weight control.
- Proper and balanced nutrition.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Avoid joint hypothermia.
- Wear comfortable shoes.
- healthy lifestyle.
in conclusion
The danger of this disease is that a person can be completely incapacitated. Knowing the symptoms of the disease, how it develops and how to fight it, it is possible to get rid of the disease in its early stages.